Register company in India: Introduction
To register company in India is a hassle-free process with Tetra Consultants’ assistance. The Government of India has introduced several amendments to its original incorporation rules which made it easier to do business in the jurisdiction. The simplified registration process has facilitated the development of a pro-business environment to encourage greater entrepreneurship and boost foreign investment. This is one of the many reasons why India has been a prime spot for companies to incorporate today. With our lean-and-mean mentality, you can rely on our team of experts to provide you with a seamless experience throughout the whole process to register company in India. Our ultimate goal is for your Indian company to be operationally ready within the stipulated time frame. Our service package includes everything you will require to set up company in India:
- Company registration with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs
- Local company secretary and registered address
- Nominee director
- Corporate bank account opening
- Financial license applications
- Annual accounting and tax services
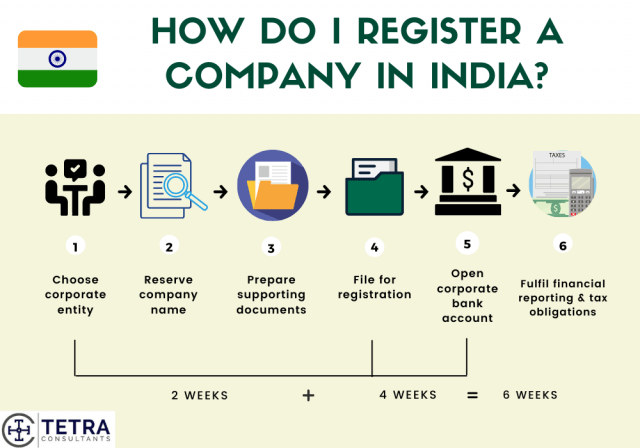
How long to register company in India and open a corporate bank account?
- Tetra Consultants will complete the process of Indian Company registration within 2 weeks.
- After receiving the required due diligence documents of the directors and shareholders, we will proceed to check on the availability of your preferred company name and prepare the required incorporation documents.
- Throughout the process of registering company in India, we will offer non-travel solutions that are meant to be convenient for you.
- After the setup is completed, we will courier the documents of your new company to your preferred address. The documents will include the Certificate of Incorporation as well as the Memorandum of Association.
- After completion of company registration in India, Tetra Consultants will open a bank account for your company. This will take around 4 weeks to complete.
- Even during the opening of the bank account, we will seek to provide you with non-travel banking solutions.
- Within 6 weeks from our engagement, you can expect your company to be fully set up and ready for business.
Can a foreigner register company in India?
- Yes, foreigners are allowed to set up business in the jurisdiction and have 100% foreign ownership of their company. Even though these companies must have at least one resident Indian director, it is still the fastest way to enter the Indian market. Satisfying this resident director requirement is easy since Tetra Consultants provide nominee director services for our International clients looking to set up company in India & carry out foreign business in the country.
- New business registration in India can also be done by choosing to register company in India in the form of a branch office, liaison office or project office. However, they will need to wait for governmental approval or approval from the Royal Bank of India. Additionally, this option is only available to stakeholders (individuals cannot open such foreign offices).
Types of business structures to register company in India?
Sole proprietorship
- In India, a sole proprietorship is the simplest business structure. Here, one person owns and controls the business. The owner is accountable for the business’s debts, and taxes based on their individual income tax return.
Partnership
- In a partnership, two or more individuals join forces to own and manage a business. Partnerships can be either general or limited, with limited partners enjoying restricted liability. The terms and conditions of the partnership are usually outlined in a partnership deed.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
- An LLP is like a mix of partnerships and corporations. Partners in an LLP have limited responsibility and can manage things. In this setup, partners are not on the hook for debts, and the rules are usually less strict than in private limited companies.
Private limited company
- A private company is a separate legal entity with shareholders and limited liability. Unlike a public limited company, it cannot offer shares to the public. Shares determine ownership, with less strict compliance compared to public limited companies.
- Various statutory requirements for private limited companies are as follows:
- A least of 2 to a most of 200 shareholders.
- A least of 2 to most of 15 directors
- No residency requirements for shareholders.
- At least one director of a private limited company must be a resident in India.
- A share capital of ten crore rupees or more must have a full-time company secretary.
- A registered office address is a mandatory need for company registration in India.
Public limited company
- Like a private company, a public limited company can sell shares on the stock exchange. Shares determine ownership, with less strict compliance compared to public limited companies.
- Various statutory requirements for private limited companies are as follows:
- A public limited company must have a least of 7 shareholders and at least 3 directors.
- At least one director must be a resident of India.
- No company secretary.
- A registered office address is mandatory for company registration in India.
Branch office
- A branch office in India is like an extension of a foreign company, doing similar business activities. The branch operates under Indian laws. The foreign company is accountable for the branch’s activities in the country.
- To register a branch office in India you will need to adhere to following requirements:
- A registered office address is a mandatory requirement for company registration in India.
- The parent company’s address can use as the registered office address for the branch office in India.
One person company
- Designed for sole entrepreneurs, an OPC is a private company formed with a single director and shareholder. It offers limited liability to the owner, and compliance requirements are less burden.
NGOs (Non-Governmental Organizations)
- NGOs are entities formed for social, cultural, economic, educational, or charitable purposes.
How to register company in India?
- Tetra Consultants advises you to read through this guide to fully understand the steps required to register company in India and simultaneous set up a bank account with the local banks in India.
Step 1: Choosing a suitable business entity before you register company in India
- After understanding your business goals and activities, our team of dedicated consultants will recommend the most suitable entity for you to carry out your business. There are many different types of company registration in India, but private limited company registration is most popular with our foreign clients since it offers ease of incorporation and liability protection. Prior to incorporating an Indian company, you will be advised on the optimum paid up share capital, company structure, legislations and whether there is a need to apply for any licenses to operate.
Step 2: Reservation of company name before you register company in India
- Before you advance to register company in India, Tetra Consultants will reserve your preferred company name with the Indian Registrar of Companies (ROC). This will be done through the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) portal. Company name registration must be completed within 20 days from the date of approval of the new name, otherwise the reservation will be released.
Step 3: Preparation of supporting documents to register company in India
- Before Tetra Consultants can set up your company in India, you are required to provide a list of required KYC documents. Some of these documents include the names of directors and identification proof.
- Proof of the registered office address must also be provided. This should be in the form of the deed of the location, or a rental agreement. Utility bills of the office should also be provided, along with a No Objectification Certificate from the landlord stating his approval for the premises to be used as an office.
- Upon receiving all the necessary documents, Tetra Consultants will proceed to draft and notarize the company’s Memorandum and Articles of Association.
- According to the business activity and company structure, Tetra Consultants will also draft articles of incorporation, business plan and other incorporation documents required to register company in India.
Step 4: Filing to register company in India
- We will then proceed to file for registration with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) portal.
- It is important to note that directors of foreign companies are not required to apply and obtain a Director Identification Number (DIN), unlike local directors. Yet, foreign directors of all company structures are still required to register for a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC). Tetra Consultants will continue to assist you with Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) applications and their requirements.
- If you are looking to set up a Limited Liability Partnership, a Designated Partner Identification Number is necessary. As such, our team of consultants will file for the identification number on your behalf.
- After receiving approval, Tetra Consultants will courier the India company registration certificate, Memorandum and Articles of Association and other documents to your preferred address.
Step 5: Corporate bank account opening
- After registration, Tetra Consultants will assist you in opening a corporate bank account. Our team has established partnerships with multiple reputable banks in India. We will present your business to each relationship manager and compliance team.
- Typically, the account opening will take roughly four weeks. In most cases, the directors and shareholders are not required to travel. However, if travel is required, we will have a representative accompany you to the bank meeting. Alternatively, our team will negotiate with the banks to conduct a conference call instead or to request a waiver.
- Some of the banks we work with include the State Bank of India, HDFC Bank, Bank of Baroda and ICICI Bank.
- Once your account has been successfully opened, Tetra Consultants will courier the internet banking token and access codes to your preferred address.
Step 6: Financial reporting and taxation obligations
- Following the setup of your new India company, Tetra Consultants will continue to provide you with the necessary accounting and tax services to ensure that you can continue to legally conduct business while staying compliant with regulatory obligations.
- Our team of dedicated consultants will prepare your firm’s financial statements, corporate tax returns and manage bookkeeping on your behalf.
- All resident companies are mandated to file annual audited financial statements with the MCA.
- It is also compulsory for you to hold minimally 1 board meeting every quarter and an Annual General Meeting within 6 months before the closing of the accounting year.
- You can expect to make direct tax payments in the form of income tax, gift tax, wealth tax, capital gains tax, corporate tax or securities transaction tax. Typically, foreign companies are charged at a tax rate of 40%.
- Other indirect tax payments may be applicable if you supply goods and services domestically. Tetra Consultants will assist with your new company GST registration in India.
- Companies may be required to obtain a Permanent Account Number (PAN) card from the Income Tax Department. A PAN card is necessary when performing financial transactions in India. In the absence of a Permanent Account Number, you may be charged with an additional withholding tax rate of 20%.
- Our team of dedicated consultants will continue to clarify any doubts you may have with regard to your company’s obligations.
Guidelines on how to choose your company name to register company in India
Unique name:
- When picking a name for your Indian company, it is crucial to choose one that is unique and not like any already registered entity. This uniqueness is essential for brand identity, making sure your company stands out in the market.
Avoid restricted words:
- Exercise caution in word choice, avoiding implications of government approval without official authorization. This preventive measure helps circumvent potential legal challenges during the company registration process.
Check availability:
- Before finalizing a name, it is prudent to verify its availability on the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA) portal. This makes sure your chosen name is one of a kind, making registration easy and lowering the chance of conflicts with other businesses.
Suffix:
- Following naming rules is vital. For private companies, the name must end with “Private Limited,” and for public ones, it should end with “Limited.” Using these suffixes is essential to state the company’s legal structure.
Reserve the name:
- Once you have picked a unique name secure it by submitting Form INC-1 to the Registrar of Companies (ROC). Taking this step prevents others from using registration and protecting your brand identity.
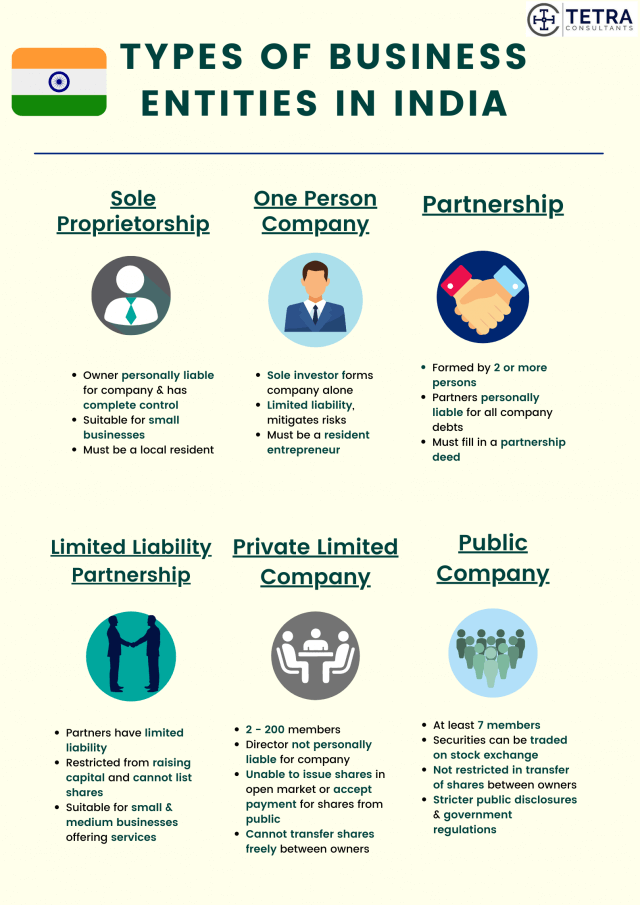
Type of business entities available for India company registration
- There are many types of business structures in India, each with its own levels of personal liability protection, tax ramifications, ownership and management flexibility, and compliance requirements.
- Before the start of the engagement, Tetra Consultants will fully understand your business before recommending the most optimum business entity in India. Some considerations we take into account include the type of business activity, tax obligations and nationalities of shareholders and directors. Our consultants will also offer more information on the requirements imposed to set up these entities.
- Generally, for most companies in India, you will only require a director and shareholder of any nationality, a local registered address and registered agent. No minimum paid-up capital is necessary for incorporation as well.
Sole Proprietorship
- The simplest form of business structure, a sole proprietorship does not separate the legal personalities of the owner and the business. While this provides greater simplicity operationally, it can cause frustrations in the event of a winding-up since the proprietor can be personally liable for all debts and obligations incurred by the business. Any transfer of business is not allowed and hence, there is no continuity. Unlike other business structures, Sole Proprietors are required to report their business income under their individual federal tax returns.
- If you are looking to set up a small business (minimart, art studio, bakery, etc.) yourself that includes the advantages of an easy startup and complete control, a Sole Proprietorship may be the business structure for you. However, it is only available to local residents.
- Owners of a Sole Proprietorship are not required to register with the government nor submit any government regulatory paperwork. These businesses also do not need to create a Permanent Account Number.
One Person Company
- Unique to the laws of India, a one-person company was introduced by the 2013 Companies Act. Under a one-person company, the sole investor can form a company alone with limited liability. This structure is meant to mitigate the risks generally faced by sole proprietors during the event of a winding-up. The risks are limited to the extent of the shares held by one such person in the company.
- While this entity is attractive, it is not available for a foreigner and is primarily meant for individual resident entrepreneurs.
Partnership
- A partnership is created and formed by two or more persons. Unlike a company, a partnership is not a separate legal entity. It is not allowed to own properties, incur debts or even sue or be sued by any other party. In the eyes of the law, a partnership is not a distinct legal entity from the partners. As such, partners of the firm can be personally liable for all the debts and obligations incurred by the business.
- To set up a partnership firm, registration is not necessary. However, it is still important that you fill up a partnership deed that will declare the duties and obligations of each partner and the profit-sharing ratio.
Limited Liability Partnership
- This company structure can be seen as the middle ground of a limited liability company and a partnership. Setting up this entity will provide its partners with limited liability. Thus, in the event of winding up, partners are protected and will not be liable for the debts and obligations. A limited liability partnership is however restricted from raising capital in the same way that a limited liability company would be, and cannot list its shares.
- Being much more flexible in nature, this entity remains ideal for small and medium enterprises. This entity would be suitable if you are looking to set up a business in the service sector or in professional services.
Private Limited Company
- This entity is made up of at least 2 members but no more than 200 members. It is not allowed to issue shares in the open market, nor can it accept payment for shares freely from the public. Shares in the company are also not allowed to be transferred freely from one owner to another.
- In the eyes of the law, this form of company is seen as a separate legal personality from its owner. Thus, in the case of a winding-up, the director will not be personally liable for any debts and obligations as incurred by the company.
Public Company
- Being publicly owned, a public company’s securities can be traded on a stock exchange. Unlike a private limited company, a public company is not restricted when it comes to transferring shares from one owner to another. Minimally 7 members are required in order to set up a public company.
- However, a public company will be subject to stricter public disclosures and comply with stricter regulations from the government authorities and its relevant departments. It will also not be covered by a privacy policy and its list of shareholders can be publicly viewed.
Why is it important to choose the right business structure?
- Choosing the right business structure in India is a crucial decision that affects the success and lasting power of a business. It goes beyond legal requirements, influencing how operations, taxes, risk management, and future growth unfold.
Compliance with legal requirements:
- Choosing the right business structure is vital to meet specific legal requirements. Failure to do so can lead to complications and non-compliance with the law. Each business structure has its own legal duties. It ensures the business runs within the rules, protecting its legal standing.
Tax efficiency:
- Diverse business structures carry distinct tax implications. Choosing a different entity exposes the business to higher taxes and financial losses. Consideration of tax is essential for optimizing financial resources as it minimizes tax liabilities and ensures the health of the business.
Operational matters:
- The choice of business structure influences day-to-day operations. It shapes the decision-making process, management structure, and the ability to raise funds. Perfect structure enhances operational efficiency and facilitates the smooth functioning of the business.
Alignment with business goals:
- Choose a business structure that fits your company’s goals and time horizon. Strategic alignment ensures a purposeful approach to achieving goals and fostering sustained growth.
Scalability:
- A good business structure should let the company grow and adjust to market changes and needs. Scalability ensures the business is right for current needs and flexible to grow and adapt to market changes.
Accounting and tax obligations after you register company in India
- Accounting and tax considerations are important factors when incorporating your company. By outsourcing your India accounting and tax obligations to Tetra Consultants, you can be confident that you will be in the best hands. Our team of consultants will ensure that your firm’s financial statements, corporate tax returns and audits are completed in a timely manner without the need for you to travel.
- Additionally, outsourcing your accounting and tax needs to Tetra Consultants will allow you to reduce overhead costs and be ensured of timely reporting and filings. Before the start of the engagement, our accounting team will also keep you updated of all the required deadlines and expectations. Thereafter, we will prepare all required filings in advance to ensure that the stipulated deadlines are met, and you will not be charged any penalty.
Documents required to register company in India
- Registering a company in India requires specific documents. Tetra Consultants can provide a customized list based on your business needs. Their expertise ensures accurate guidance on the specific paperwork your business requires. Tetra Consultants help you register your company, providing the essential documents you need.
- For directors and shareholders:
- Passport, POA, CV and POI
- Memorandum of Association (MOA)
- Articles of Association (AOA)
- Proof of registered office address
- Digital Signature Certificate (DSC)
- Directors Identification Number (DIN)
- Certificate of Incorporation
Annual Reporting Requirements
- Typically, an Indian business entity’s financial year runs from 1 April to 31 March.
- All Indian companies are required to prepare and submit separate and consolidated financial statements to the MCA within 6 months from the end of the financial reporting year. These statements should include a balance sheet, statement of profit and loss, changes in equity, cash flow statement and relevant disclosures.
- Under the Income tax Act, companies may have to get their accounts and tax filings audited. This report will be submitted to the Income Tax Department.
- You will also have to maintain and record all books of accounts and other necessary documents. This may be required to compute taxable income.
- It is also compulsory for your business to hold minimally 1 board meeting every quarter and an Annual General Meeting within 6 months before the closing of the accounting year.
- Tax payments may come in the form of direct taxes and indirect taxes.
Corporate Income Tax
- Generally, all foreign companies are mandated to a tax rate of 40% while domestic companies are charged between 25% to 30%.
- You can expect to enjoy various rebates if you decide to set up new sources of power or infrastructure or to venture into capital enterprises or funds.
Minimum Alternate Tax
- Additionally, India adopts a Minimum Alternate Tax regime. Under this rule, taxpayers with substantial income cannot avoid tax liability. The amount of tax per charged will be based on the book profit and compared to the income tax that is to be paid on the total income. It is to note that, foreign companies that are resident in a country with which India has a Double Tax Avoidance Agreement will not be subjected to the Minimum Alternate Tax rules.
- Typically, the Minimum Alternate Tax Rate is charged at 18.5% of book profits.
Dividend Distribution Tax
- This tax is charged based on the dividend distributed to shareholders in a particular year.
Capital Gains Tax
- In India, this is classified based on the type of gains – short-term or long-term. An asset is classified as a long-term gain if it is held for more than 3 years. Long-term gains are typically charged at a higher rate as compared to your short-term capital gains.
Why set up company in India?
Before you begin to register company in India, it is important to understand the business landscape of the jurisdiction. This is to ensure that your newly established entity will be able to safely and legally conduct business while striving towards your long-term business goals.
Political
- Progress has been made by the country when it comes to corruption and bribery issues. In preventing and limiting these issues, the jurisdiction is constantly amending the Prevention of Corruption Act to ensure its relevancy and enforceability.
- A survey conducted by Transparency International India and LocalCircles found that while cases of bribery in India have reduced, it is still largely present within the society with as much as 51% of respondents having paid bribes before.
- While India constitutionally allows freedom of speech and expression, it also permits the government to limit freedom of expression. This has led to the suppression and silencing of free speech within its society.
Economic
- Possessing a large labor pool, costs of labor are amongst the lowest in India. As such, if your business is labor-intensive, locating in India may be ideal for you.
- India is home to many Special Economic Zones that are set up for the purpose of promoting a competitive environment and boosting industrial progress within the nation.
- According to Institute for Management Development’s 2021 World Competitiveness Index, India is ranked 43rd.
Social
- The 2019 Multidimensional Poverty Index released by the United Nations Development Programme highlights that India has been a notable example in tackling poverty. The report found that an estimated 271 million have been successfully lifted out of multidimensional poverty.
- India’s official languages include both English and Hindi. While English remains its official language, only an estimated 10% of its population are proficient in it. This may result in potential inconvenience when communicating and transacting with the local government and banks.
- Peace in India is often short-lived. In the recent 2020 Delhi Riot, unhappiness sparked between the Hindu mobs and Muslims led to a violent riot, causing many casualties.
Technological
- The information technology industry in India is a growing sector. The industry in itself has progressively increased its contribution to India’s Growth Domestic Product has increased from 1.2% in 1998 to 7.7% in 2017.
- In 2019, the Global Innovation Index ranked India 3rd in the world when it comes to attracting foreign investment for technology transactions.
- India is home to many tech talents, prompting many Southeast Asian Startups such as Gojek to be constantly on the hunt for Indian tech talents.
Legal
- In recent times, India has been trying to improve its standing with regard to international arbitration. This is achieved by introducing several amendments to the Act. These amendments are setting a shorter timeline to conclude disputes, creating more certain laws and ensuring greater enforcement.
- When it comes to commercial disputes, Indian courts have been notorious for delaying cases. Hence, if you do land yourself in a commercial dispute, these delays may be frustrating.
- Corruption in India’s judiciary is a notorious fact. In 2010, a former Law Minister shared that 8 out of the 16 former Chief Justices of India employ corrupt practices.
Environmental
- Progress has been made when it comes to increasing India’s environmental efforts. This includes a pledge to ban single-use plastic by 2022 and greater efforts in cleaning up public spaces and ensuring hygiene.
- India’s investment in renewable energy is commendable. Karnataka, a state in India, sources 27% of its energy sustainably through renewable energy sources.
- According to the World Health Organisation, 14 of the world’s most polluted cities can be found in India.
Find out more about how to register company in India
- Tetra Consultants will be your one-stop solution for you to register company in India. Our services include company formation, registered agent, registered address, and business bank account opening.
- Contact us to know more about how to register a company in India. Our dedicated and experienced team will revert within the next 24 hours and answer all your queries.
Contact us to know more about how to register a company in India. Our dedicated and experienced team will revert within the next 24 hours and answer all your queries.
FAQ
What is the best business in India?
- Given the size of the domestic market in India, there are many good businesses that companies can choose to do.
- India is the world’s biggest manufacturer of generic drugs, and the second-largest food and agricultural producer. Its telecommunication industry is the second largest as well.
How much does it cost to start a business in India?
- While there are no paid-up capital requirements, Tetra Consultants will recommend setting aside at least US$5,000 as your paid-up capital to fund your overhead expenditures as well as initial deposit for business bank account opening.
- As for Tetra Consultants’ engagement fees, this depends on the exact services required from Tetra Consultants. Our fees are inclusive of government fees and all fees will be clearly stated in our engagement letter prior to the start of the engagement. Tetra Consultants believes in transparency with our valued clients and there are no hidden fees.
How can I check the status of my company in India?
- You can use the online search function on the MCA portal website.
Do I need to register even if my business is an online business?
- Yes, it allows you to legally use your business name.
When is Goods and Service Tax registration compulsory?
- When company turnover exceeds 20 lakh rupees (US$27,500) or for certain business activities.
What is a lakh?
- One lakh is equivalent to 100,000 rupees or US$1500.
What is a crore?
- A crore is equivalent to 100 lakhs, or 10,000,000 rupees. The equivalent value is US$140,000.
What are some examples of GST exempted goods in India?
- Maps, books, journals and newspapers are all considered to be GST exempt.
What is a DIN and DSC?
- A DIN stands for a Director Identification Number, which local directors of One Person Companies, Private Limited Companies or Limited Companies in India must have. A DSC, on the other hand, refers to a Digital Signature Certificate, which all directors of India companies, whether local or foreign, will have to possess. The DSC Digital Signature Certificate will be needed in the application for the DIN.
- Both the DIN and DSC can be applied for with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA). Tetra Consultants will assist you with both DIN and DSC applications and their requirements.